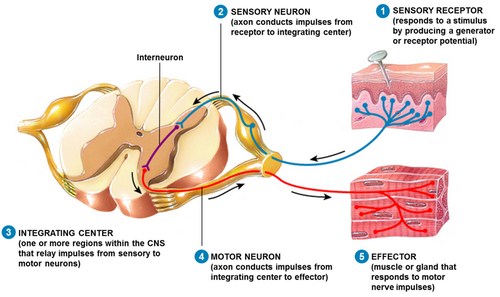
When nervous system exerts its action over the other systems of body, most simplified form of its action is manifested basically as:
- Contraction of muscles.
- Secretion of exocrine glands.
It may be noted here that the secretion of endocrine glands is mostly under the hormonal control.
The muscles, whose contraction is regulated by nervous system, may be voluntary (striated or skeletal) or involuntary (nonstriated or smooth). Contraction of the voluntary muscles results in movement of a joint. The involuntary muscles may be in the wall or in the substance of viscera, which are specifically called ‘Visceral muscle’, e.g. in the wall of the gastrointestinal tract, or tracheobronchial tree or in the substance of any solid viscera. Again, the involuntary muscle may be in the wall of the cardiovascular channel, e.g. in the wall of the heart (myocardium) or in the wall of blood vessel (tunica media). It may be also in the dermis of the skin named the Arrectores pili.The exocrine glands influenced by the activity of the nervous system may be single and solitary like any salivary gland or the lacrimal gland, or it may be multiple and minute, like the mucous glands of the wall of GI tract, or respiratory tract.
So result of functions of nervous system may be summarized as follows:
- Contraction of voluntary muscle(s): Resulting movement of a joint. It may result movement of some organs, like tongue, eyeball.
- Contraction of involuntary muscle(s) present in:
- Viscera: It is called visceral muscle.
- Wall of the cardiovascular system: Myocardium of heart or smooth muscle in the wall of the blood vessels.
- Dermis of skin called Arrectores pili: It is attached to the root of hair follicle.
- Secretion of exocrine glands like:
- Salivary glands or lacrimal gland: Large and solitary.
- Mucous secreting glands: In the wall of GI tract or respiratory tract–many and minute.
But it is to be noticed that the functions of nervous system do not mean only the effects as mentioned above, but, in gist it also performs the followings:
- It receives and carries different information from its periphery to center, which are related to change in external and/or internal environment.
- It perceives or acknowledges the informations at its center.
- It analyzes, integrates and coordinates the informations or inputs.
- It commands for some effect after reception and, integration or coordination of informations.
- It stores the informations for the memory, intelligence, learning and emotion of an individual.
Source: Easy and Interesting Approach to Human Neuroanatomy (Clinically Oriented) (2014)