Effectors are the specialized junctional areas where terminal ends of motor nerve fibers come in contact with effector organs. These effector organs are of following three types:
- Somatic effectors: These are skeletal muscle fibers (myocytes) which receive terminal ends of somatic motor nerve fibers. These specialized sites are known as somatic neuromuscular or myoneural junctions.
- Visceral effectors: These are smooth muscle fibers (myocytes) which receive terminal ends ofautonomic motor nerve fibers (sympathetic or parasympathetic). These specialized junctional sites are known as visceral neuromuscular or myoneural junctions.
- Secretomotor effectors: These are specialized junctional areas between secretomotor autonomic nerve endings and specialized contractile cells in the walls of alveoli (acini) of exocrine glands. These contractile cells are known as myoepithelial cells.
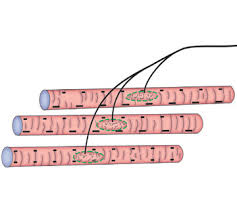
Each of the somatic (skeletal) muscle fibers gets direct contact with endings of motor nerve fibers for innervation. This site of contact is called neuromuscular junction or myoneural junction.
These muscle fibers are of two types:
- Extrafusal fibers: Which receive endings of alpha neuron
- Intrafusal fibers: Which receive endings of gamma neuron. It has already been studiedthat both terminal contractile ends of intrafusal fibers receive gamma motor nerve endings.
- Motor end plates or ‘en plaque’ endings: Most of the myoneural junctions are of this variety. In these types, the axon terminal of a motor nerve comes to an oval specialized area of a muscle fiber at its center. This specialized oval area at the surface of muscle fiber is called sole plate. The junctional area between sole plate and axon terminal is known as motor end plates.
- ‘En Grappe’ endings: In this variety, axon terminal runs along the length of muscle fiber. While running along, it divides, into series of short branches which end into ‘knob-like’ endings on the surface of muscle fiber.
- Trail endings: In this type, axon terminal run along the length of muscle fibers and end in multiple finer endings.
‘En Grappe’ and trail endings are found in intrafusal fibers of muscle spindles.
Source: Easy and Interesting Approach to Human Neuroanatomy (Clinically Oriented) (2014)