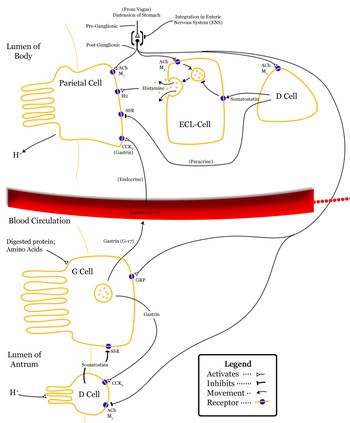
This is secreted from the G cells of pyloric antral mucosa. This region has a neural crest origin and is capable of taking amine precursors and decarboxylate them. That’s why these cells are called APUD cells (amine precursor uptake and decarboxylation). Gastrin secreting cells are also found in other regions like stomach and intestine which is not physiologically significant. The gastrin that is secreted from G cells of pyloric antrum has 17 amino acid residues (G17). It is the principle form of gastrin, which stimulate gastric acid secretion and pepsin. The other gastrins are G34 and G14 secreted from the other regions. Gastrin secreting tumors (gastrinomas) can be found in pancreas. G17 has a half life of 2 to 3 minutes in the circulation.
the principle form of gastrin, which stimulate gastric acid secretion and pepsin. The other gastrins are G34 and G14 secreted from the other regions. Gastrin secreting tumors (gastrinomas) can be found in pancreas. G17 has a half life of 2 to 3 minutes in the circulation. Secretion of gastrin occurs due to:
- Distention of stomach
- Presence of protein and products of proteine breakdown
- Stimulation of postganglionic parasympathetic vagal endings supplying the pyloric
antrum. The transmitter that is released is not acetyl choline, but GRP (gastrin releasing peptide). This peptide causes the secretion of gastrin. - Blood borne factors like Ca++, epinephrine.
- Amino acids especially tryptophan and phenylalanine
Presence of acid in the stomach has a negative feed back control, which inhibits gastrin secretion. Blood borne substances like secretin, GIP (gastric inhibitory peptide), VIP, glucagon and calcitonin inhibit gastrin secretion.It has many forms, similar to gastrin, ie, CCK 8, CCK 12. Its half life in the circulation is 5 minutes. CCK is cholecystokinin, which causes the gallbladder contraction and release of bile. The same hormone acts on the acinar cells of the exocrine pancreas and produces pancreatic secretion rich in enzymes. Hence, CCK is also called pancreozymin. Since both are one and the same, it is commonly referred as CCK- pancreozymin. CCK is secreted from the mucosa of the upper part of small intestine, from nerve endings in distal ileum, colon and neurons in brain.
Actions of gastrin:
- Stimulates enterochromaffin like cells( ECL) to secrete histamine
- Stimulates growth of mucosa in the stomach and small intestine
- Causes secretion of gastric acid and pepsin
- Stimulates gastric motility
- Stimulates insulin secretion after a protein meal.
Source: Textbook of Physiology, 3E (Chandramouli) (2010)