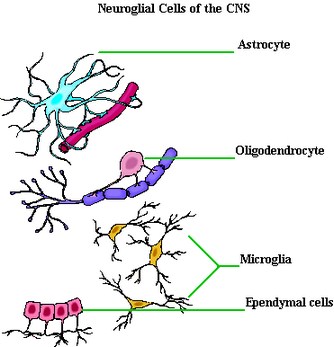
In central nervous system
- Ependymal cell
- Macroglia – a) Astrocytes b) Oligodendrocytes
- Microglia.
- Schwann cells.
- Satellite cells.
These are single-layered cubical or columnar cells lining the cavities (ventricles and central canal) of central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). They represent the original cells lining the neural tube of embryonic life. The free surface of the cells present ultramicroscopic finger-like prolongations which are nonmotile in nature. These are known as stereocilia.
Functions:
- Stereocilia of free surface of ependymal cells increase surface area, so help in absorption of cerebrospinal fluid circulated in cavity of central nervous system.
- Specialized area of ependymal lining of ventricles is also concerned with formation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
These cells are so-called because they are star-shaped with radiating cytoplasmic processes. Astrocytes are of following two types.
Oligodendrocytes
These are smaller round or spherical cells with lesser number of processes. They are found in white matter of central nervous system where expanded end of their processes wrap around the length of nerve fibers. This wrapping (ensheathment) or insulation of nerve fibers is known as Myelination. The myelination prevent the nerve impulse to be dissociated to the surrounding tissue and thus facilitate the full conduction of impulse towards the destination.
Functions:
- Coffee
- Tea
- Milk
2. They form myelin sheath around nerve fibers (processes of neurons) inside central nervous system.
Microglia
Microglia are so-called because they are smaller in size. The cells present finer tortuous processes. Microglia are identified by following three characters which are related to the letter ‘M’.
- Microglia are Mesodermal in origin which develops from circulating Monocytes of fetal blood.
- Microglia function as Macrophages of central nervous system to engulf toxic substances, microorganism and damaged CNS tissue debris.
- For phagocytic function, microglia are Migratory in nature. Many microglia, acting as scavenger cells are localized at the site of damaged or degenerated nerve tissue and may fuse together to form a Multinucleated giant cell of central nervous system.
Schwann cells
These are the neuroglial cells found in peripheral nervous system, related to peripheral nerve fibers. The cells are flattened with adequate amount of cytoplasm surrounding nucleus. The surface of the cell is invaginated by processes of neuron. The nerve fiber, following invagination, undergoes spiral movement to be finally wrapped by layers of Schwann cells which finally acts as myelin sheath.
Function: Many Schwann cells in a row, take part in formation of myelin sheath of peripheral nerves outside central nervous system.
Source: Easy and Interesting Approach to Human Neuroanatomy (Clinically Oriented) (2014)