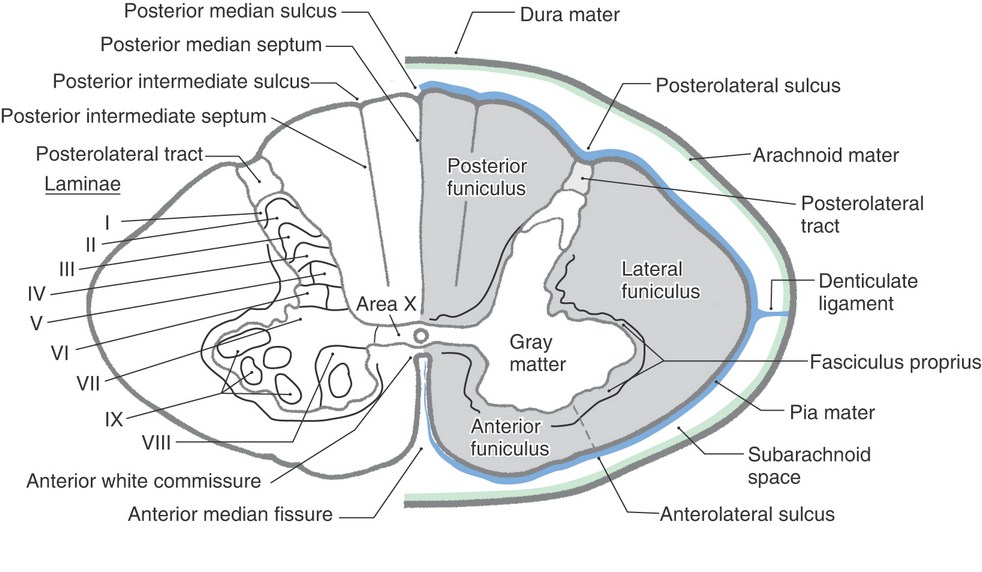
On cross-section of spinal cord, cells of various columns of spinal gray matter represent a strip-like appearance which is called Rexed lamination. Theselaminae are ten in number, which are sequentially numbered from the dorsal horn side towards ventral horn, as per Roman numerals.
The cells of these laminae are classified according to shape, size, density and cytological characteristics. These laminae corresponds more or less to the different cell-groups stated earlier.
- Lamina I: It is also called lamina marginalis. It is a very thin layer on the tip of dorsal horn. This lamina is composed of cells of different size and shape with intermingling fibers giving a reticular appearance.
- Lamina II: It is made up of densely packed and darkly stained cells with nonmyelinated fibers. It is a part of substantia gelatinosa.
- Lamina III: It is made up of loosely packed and large sized cells with myelinated fibers. This lamina is made up of cells of nucleus proprius and some cells of substantia gelatinosa.
- Coffee
- Lamina IV: It is thick and homogeneous lamina forming nucleus proprius.
- Lamina V and VI: These two laminae constitute base of posterior horn. Cells of this laminae receive,
- Afferent fibers carrying proprioceptive sensations and sensation from viscera.
- Projections from corticospinal tracts which suggests that they are concerned with regulation of movement.
- Lamina VII: It contains following cell group:
- Intermediolateral cell group: Cells of sympathetic center of autonomic nervous system.
- Intermediomedial cell group: Cell forming spinal parasympathetic center of autonomic nervous system.
- Clarke’s column of cells.
- Lamina VIII: It is made up of interneurons which receive terminals from:
- Cells of adjacent laminae of same side
- Cells of lamina VIII of opposite side through gray commissures.
- Lamina IX: This lamina presents lateral and medial strips which are made up of:
- Alpha and gamma motor neurons
- Interneurons.
- Lamina X: These are the nonspecific cells of anterior and posterior gray commissures encircling central canal.
Source: Easy and Interesting Approach to Human Neuroanatomy (Clinically Oriented) (2014)