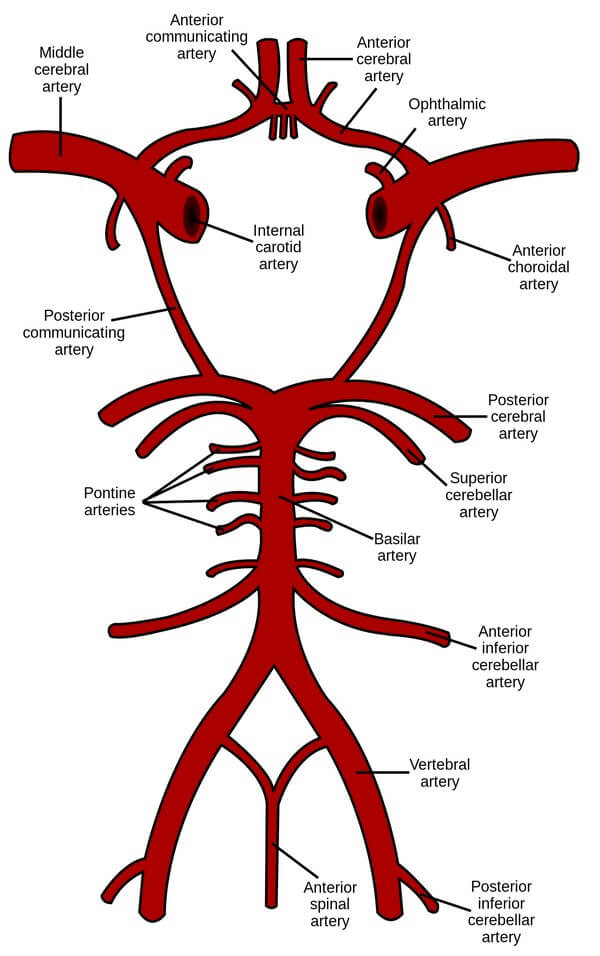
It has already been learnt that, brain receives two sets of branches from arteries of both vertebrobasilar and carotid system. These are cortical and central. Branches from circle of Willis are all central. These are also called nuclear or ganglionic branches which are example of end arteries. Branches are divided into following four groups.
- Anteromedial—Median
- Anterolateral—Right and left
- Posteromedial—Median
- Posterolateral—Right and left.
These branches arise from anterior communicating and anterior cerebral arteries. One of the branches arise from anterior cerebral artery which presents a recurrent course. This is called recurrent artery of Heubner. Anteromedial set of branches supply—
- Anterior half of anterior limb of internal capsule
- Putamen
- Head of caudate nucleus.
Anterolateral branches
These are called striate arteries which arise from site of origin of middle cerebral artery. These branches penetrate through anterior perforated substance and are divided into two groups called lateral and medial striate arteries. Lateral striate arteries ascend along lateral surface of lentiform nucleus. These arteries supply—
- Posterior half of anterior limb and anterior twothirds of posterior limb of internal capsule
- Lentiform nucleus
- Caudate nucleus
- Thalamus.
One of the lateral striate arteries supplying posterior limb of internal capsule presents a long course. It is called Charcot’s artery of cerebral hemorrhage. Because of its length, it is more prone to be damaged in cerebrovascular accident. Medial striate arteries ascend medial to lentiform nucleus and supply Caudate nucleus and Internal capsule.
Posteromedial branches
These branches are median in position and originate from posterior communicating and posterior cerebral arteries. They penetrate through posterior perforated substance and give branches to
- Anteromedial part of cerebral peduncle
- Hypothalamus forming floor of third ventricle
- Medial part of thalamus forming lateral wall of third ventricle.
Posterolateral branches
These branches arise from posterior cerebral artery lateral to its junction with posterior communicating artery. Posterolateral branches are bilateral to supply:
- Posterior part of thalamus
- Geniculate bodies
- Posterior part of cerebral peduncle
- Pineal gland
- Tactum of midbrain.
Central branches of circle of Willis are also known as ganglionic or nuclear branches, because in the central core of brain, these branches not only supply important fiber bundles like internal capsule, but also many of them supply submerged collection of gray matter which are called basal ganglia or basal nuclei. All the central branches are example of end arteries having no anastomosis in precapillary level. So, once one of these arteries are affected due to hemorrhage, thrombosis or embolism, area of brain supplied by that artery will suffer from irreversible damage.
Source: Easy and Interesting Approach to Human Neuroanatomy (Clinically Oriented) (2014)