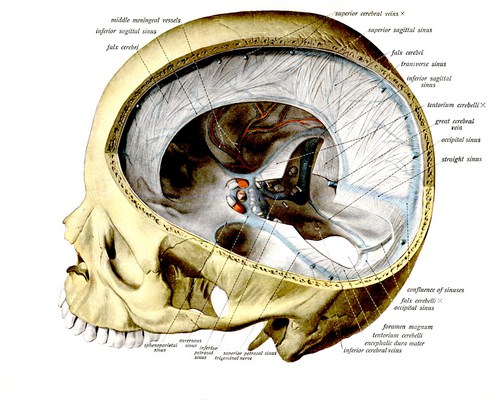
These are formed when meningeal layer gets separated from endosteal layer to invaginate in the gaps (sulci or fissures) between adjacent parts of brain.
Important dural septae or fold are:
- Falx cerebri
- Tentorium cerebelli
- Falx cerebelli
- Diaphragma sellae.
It is a sickle-shaped fold of dura mater which extends anteroposteriorly, through midsagittal plane and dips in median longitudinal fissure of brain between two cerebral hemispheres.
- Ends: Anterior apical end is attached to crista galli of ethomoid and adjacent part of internal crest of frontal bone. Posterior basal end is anteroposteriorly running straight border which is attached to midline of superior surface of tentorium cerebelli.
- Borders: Superior border is convex and attached to margins of a narrow linear sulcus on the inner surface of median sagittal sutures connecting two parietal bones. Inferior border is concave and comparatively sharper free border which comes in relation to anteroposteriorly convex superior surface of corpus callosum.
Tentorium cerebelli
It is a double fold of dura mater which invaginates horizontally forwards through the gap between the occipital lobes of cerebrum and cerebellum. Tentorium cerebelli is so called because from midline it slopes on either side downwards and laterally to adjust the slopes from raised superior vermis to superior surface of cerebellar hemispheres on either side.
Falx cerebelli
It is a small, crescentic fold of dura mater which extends along the midline vertical plane forwards between two cerebellar hemisphere bellow tentorium cerebelli. Superior margin is anteroposteriorly straight. It runs along midline being attached on the undersurface of tentorium cerebelli. Posterior margin is convex and attached to internal occipital crest. This margin lodges occipital sinus. Anterior margin is concave and free. It invaginates through the gap between posteroinferior aspect of two cerebellar hemispheres. Occipital sinus is lodged between right and left layers of this dura fold.
Diaphragma sellae
It is a small, round and horizontal fold of dura mater whose peripheral margin is attached to the outline of hypophyseal fossa (sella turcica) of superior surface of body of sphenoid on middle cranial fossa. It presents a central circular aperture through which infundibulum (stalk) of pituitary gland passes upwards to be attached to the base of brain.
Source: Easy and Interesting Approach to Human Neuroanatomy (Clinically Oriented) (2014)