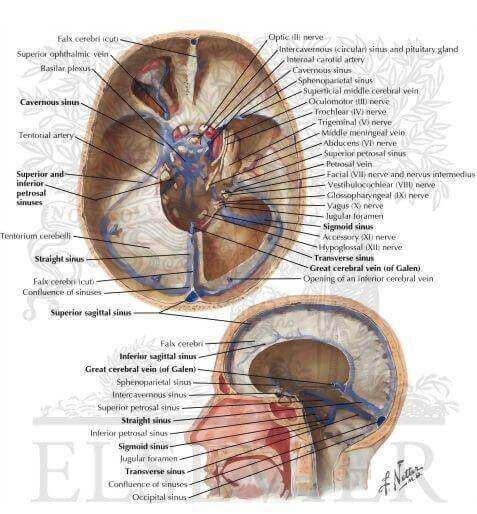
These are intracranial venous channels between endosteal and meningeal layer of cranial dura mater. These are formed due to separation of two layers or invagination of meningeal layer from endosteal layer of dura mater.
Characteristics of venous sinuses
- These are thin-walled with absence of muscle fibers in their wall.
- They are devoid of valves, so blood can flow in both directions.
- Walls are formed by dura mater with inner endothelial lining.
- The venous sinuses communicate with the veins outside cranium through emissary veins which adjust intracranial venous pressure.
- Venous sinuses receive venous blood from brain, meninges, bones of the cranium.
- Circulated cerebrospinal fluid also finally drains into venous sinuses.
- Blood from all venous sinuses finally drains through internal jugular vein.
Superior sagittal sinus
It is anteroposteriorly directed along the superior convex margin of falx cerebri. Narrower anterior end communicate with nasal veins through foramen cecum. Posteriorly at the level of internal occipital protuberance it usually turns to the right to become continuous with right transverse sinus. Cerebrospinal fluid is absorbed through arachnoid villi projecting to the wall of this sinus.
Inferior sagittal sinus
It also runs anteroposteriorly along the lower concave free margin of falx cerebri. It joins with great cerebral vein of Galen to form straight sinus.
Straight sinus
It is so called because of its straight anteroposterior midline direction along the line of attachment of falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli. It is formed by union of inferior sagittal sinus and great cerebral vein. Its posterior end turns to the left to become continuous with left transverse sinus.
Sigmoid sinus
It is so called because of its sinuous or S-shaped appearance. It is lodged on a deep groove on inner aspect of mastoid part of temporal bone. Sigmoid sinus on either side starts as a continuation of transverse sinus and continues as upper end (superior bulb) of internal jugular vein just beyond the level of jugular foramen.
Superior petrosal sinus
Superior petrosal sinus is also bilateral sinus. It is situated along the superior border of petrous part of temporal bone at the anterior part of peripheral fixed border of tentorium cerebelli. It extends from posterior end of cavernous sinus to lateral end of transverse sinus at its junction with sigmoid sinus. Blood is drained in anteroposterior direction from cavernous sinus towards transverse sinus.
Inferior petrosal sinus
This paired sinus extends from before backwards along the groove between inferior border of petrous part of temporal bone and clivus of sphenoid bone. It drains blood from cavernous sinus to bulb of internal jugular vein passing through anterior compartment of jugular foramen.
Source: Easy and Interesting Approach to Human Neuroanatomy (Clinically Oriented) (2014)