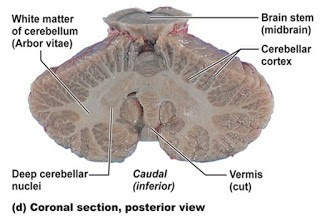
Cerebellum is structurally made up of following two
fundamental zones.
- Outer layer of gray matter called cerebellar cortex.
- Inner central core of white matter which presents a pattern like branching of a tree projecting superficially beneath the cortex of each and every folium, called arbor vitae cerebelli.
Inside the substance of white matter are embedded mass of gray matter called cerebellar nuclei.
- Outer molecular layer: Stellate cells and busket cells.
- Intermediate layer of Purkinje cells: Purkinje cells.
- Inner granular layer: Granule cells and Golgi cells. Neuroglia are present in all the layers.
- Some of cerebellar afferent relay in Purkinje cells reaching upto superficial molecular layer.
- Some afferent reaching the innermost granular layer relay in granule cells which pass further superficially to relay in Purkinje cells dendrites in molecular layer.
But this impulse is limited time to time by inhibitory influence of stellate cells, busket cells and Golgi cells of cortex on Purkinje cells, so also on cells of cerebellar nuclei.
Source: Easy and Interesting Approach to Human Neuroanatomy (Clinically Oriented) (2014)